In our previous episode, we noted how the pitfalls of the traditional finance market birthed the idea of a progressive financial protocol. And disclosed how DeFi bridges the gap between the banked and the unbanked. Simply put, learning DeFi opens all the windows of opportunities that the decentralized financial system offers to everyone.
This article will look at the fundamental concepts of the decentralized market, blockchain technology, and how to get started with DeFi.
Content:
Who needs DeFi?
What is decentralization?
What is the blockchain?
What is a smart contract?
What is a token?
What are Stablecoins?
What are dApps? (Decentralized Exchange Apps)
Who needs DeFi?
Basically, everyone who is looking to create wealth, save money, and make use of financial services like taking a loan or transferring money in today’s world should learn about the DeFi market and how decentralization benefits them. DeFi opens the finance market to all classes of people—students, traders, salary earners, etc.—regardless of their current financial capacity.
What is Decentralization?
The point of decentralization is to disintegrate the power and control that centralized bodies hold over the financial market. In a blockchain, decentralization refers to the transfer of control, supervision, and decision-making from a centralized entity (individual, organization, government, or group) to a distributed network.
What is a blockchain?
Let’s take for example a document on Google Docs or Google Sheets shared with four editors—Jack, Jane, Jake, and Jill. All editors can access the document, and the alterations and suggestions from each contributor are visible to all parties connected to the document.
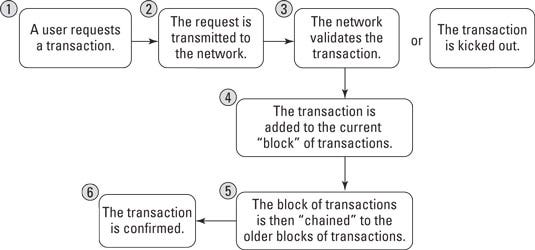
Similarly, a blockchain is a distributed database that is shared and accessible by all the nodes connected in a computer network.
In the blockchain, transparency is paramount as all the transactions and information shared in the network are easily retrievable by anyone within the network. This makes it difficult or impossible to change, intercept, hack, or alter the system.
How does a blockchain work
What is a Smart Contract?
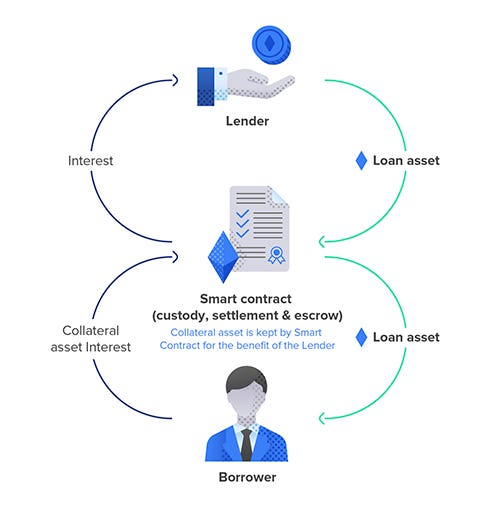
A smart contract is a digital contract. It holds the terms of an agreement between a seller and a buyer and is written directly in lines of code and executed automatically in the blockchain upon request. They are typically used to automate the implementation of an agreement so that all parties are certain of the outcome, without any interference from an intermediary or delay in the time of execution.
What is a Token?
Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and co-run on their own blockchains, but not tokens. A token is a digital asset built on a cryptocurrency's blockchain.
DeFi tokens are built as a diverse set of native products that represent these decentralized platforms that function with the use of smart contracts. These tokens provide users—who hold them in their wallets—access to an array of financial applications and services built on the blockchain.
Tokens represent digital tradable assets. They can be used as a store of value and also exchanged for stablecoin or fiat currency. Examples are Shiba Inu, Poocoin, Samoyedcoin, Joe, etc.
What are Stablecoins?
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency that has its market value pegged to other external assets, usually the fiat currency like the US dollar, euros, or gold. They help to curb the wild volatility that exists in the exchange of digital assets.
By design, stablecoins have a fixed, stable price and play a vital role in facilitating financial services like trading, lending, and borrowing of other digital assets.
Companies that issue stablecoins are required to deposit around 150% of the coin's supply in US dollars as collateral to a central financial reserve in order to maintain the 1:1 exchange rate.
Types of stablecoins
Centralized stablecoins: are issued and pegged 1:1 to a traditional fiat currency e.g. USDC, USDT.
Decentralized stablecoins: can be crypto-collateralized or algorithmic pegged to another digital asset e.g. UST, Frax.
What are dApps?
A dApp refers to a software application that’s developed over a decentralized network rather than on a single computer. Decentralized applications or dApps have similarities with traditional software applications, but they’re built and operated on distributed blockchain networks rather than central servers. Anyone with access can participate in a wide range of financial services.
For example, on a DeFi lending platform, anyone can borrow funds without an intermediary and offer their crypto tokens on the platform for lending. A borrower will directly take a loan via Peer-to-Peer lending using a smart contract.
Lending platforms such as Compound and Aave offer crypto loans whose interest rates dynamically change according to the cryptocurrency’s supply and demand. These DeFi platforms accept collateral in crypto.
Top DeFi dApps on popular blockchains
Ethereum: UniSwap, SushiSwap
Binance Smartchain: PancakeSwap
Solana: Raydium Dex
Fantom Chain: SpookySwap, WigoSwap
AVAX C-Chain: Trader Joe
Tron Chain: SunSwap
Polygon: QuickSwap
In our next episode, we'll take a deep dive into some of the top decentralized financial exchange dApps, discuss market capitalization, total volume locked, their governance tokens, and the various operations that can be accessed on these platforms. This will prepare you to understand the different ecosystems, how to use the research tools, and safely trade on these applications.
Trivia Question - What’s a stablecoin? Give an example